Robotic Total Hip Replacement
What is Robotic Total Hip Replacement?
Robotic Total Hip Replacement is a surgical procedure that uses a computer-guided robotic arm to assist the surgeon in hip replacement surgery. The robotic arm is controlled by the surgeon, who uses a specialised software program to plan and execute the surgery more accurately and precisely than traditional techniques. It uses real-time feedback and imaging technology to adjust the position and angle of the implant and ensure optimal fit and alignment. The robotic arm is not autonomous and only performs the surgery with the surgeon's expertise, guidance and control.
MAKO STRYKER TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT VIDEO HERE
Who is Suitable for Robotic Total Hip Replacement?
Robotic Total Hip Replacement may be suitable for patients with severe hip joint damage or arthritis who have not responded to non-surgical treatments, such as medication, physical therapy, or intra-articular injections. It is also suitable for patients with complex hip joint anatomy or previous hip surgery who may benefit from enhanced precision and accuracy.
What are the Benefits of Robotic Total Hip Replacement?
Robotic Total Hip Replacement offers several potential benefits over traditional hip replacement surgery, including:
- Increased precision and accuracy: Allows the surgeon to plan and execute the surgery with greater precision and accuracy, leading to a more customised and optimal fit and alignment of the implant.
- Reduced risk of complications: This may reduce the risk of complications, such as implant malposition, leg length discrepancy, and dislocation, by ensuring that the implant is placed in the correct position and angle.
- Faster recovery and rehabilitation: This may lead to a faster recovery and rehabilitation, as it causes less soft tissue damage, bleeding, and pain than traditional techniques.
- Long-lasting results: This may provide long-lasting results, with a lower risk of revision surgery or implant failure in the long term.
Alternative Options to Robotic Total Hip Replacement
While Robotic Total Hip Replacement offers several potential benefits over traditional hip replacement surgery, it may not be suitable for all patients, and alternative options may be available. Here are some of the alternative options to Robotic Total Hip Replacement:
- Traditional hip replacement surgery: Remains a widely used and effective technique to relieve hip pain and restore function for patients with severe hip joint damage or arthritis. In traditional hip replacement surgery, the surgeon uses manual techniques and instruments to remove and replace the damaged joint with an artificial implant.
- Hip resurfacing surgery: A technique that preserves more of the patient's natural bone and cartilage than traditional hip replacement surgery by resurfacing the damaged hip joint with a metal cap and liner instead of replacing the entire joint. Hip resurfacing surgery may suit younger and more active male patients who want to maintain mobility and avoid long-term implant wear risks.
- Non-surgical treatments: Non-surgical treatments, such as analgesia and anti-inflammatories, physical therapy, and weight loss management, can be effective in relieving hip pain and improving function for some patients with mild to moderate hip joint damage or arthritis. Non-surgical treatments can be less invasive and costly than surgery and usually is recommended first. They may be suitable for patients who want to avoid surgery or have medical conditions that prevent them from undergoing surgery.
Preoperative Preparation
- Your surgeon will perform a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health, medical history, medications, and any underlying conditions that may affect the surgery or anaesthesia.
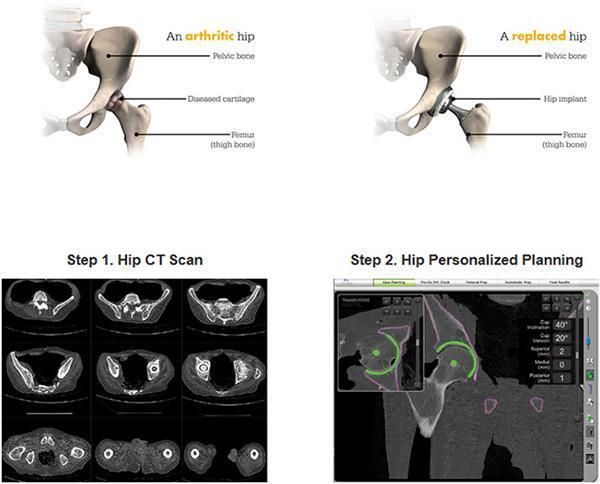
- Your surgeon will obtain X-rays and CT scans to evaluate the condition of your hip joint and create a 3D virtual model for preoperative planning.
- You may need to stop taking certain medications before the surgery, such as blood thinners or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to reduce the risk of bleeding or other complications. Your surgeon will provide you with specific instructions regarding medication management before the surgery. Also, check with your GP if some medications can be interrupted before surgery.
- You must fast for a certain period before the surgery, typically 6-8 hours, to reduce the risk of aspiration during anaesthesia.
- You may need to make some lifestyle modifications before the surgery, such as quitting smoking for at least six weeks, losing weight, or modifying your home environment to accommodate the surgery and rehabilitation.
- Your surgeon will provide preoperative education and instructions to prepare you for the surgery, including what to expect before, during, and after the surgery and how to manage pain and recovery.
- You will need to arrange transportation to and from the hospital and for someone to assist you during the early stages of recovery.
Robotic Total Hip Replacement Surgery
- Before the surgery, your surgeon will obtain a CT scan to create a 3D virtual model of your hip joint. The virtual model allows the surgeon to plan the implant's optimal position and size and creates a customised surgical plan for your specific anatomy.
- You will receive either general or regional anaesthesia, depending on your preference and medical condition. Your anesthesiologist will monitor you closely throughout the surgery to ensure your safety and comfort. When indicated, regional spinal anaesthesia reduces your risk of perioperative complications.
- Your surgeon will make a small incision, typically 3-4 inches long, on the side of your hip. After mapping your hip, the surgeon performs a cut in the femoral neck for sequential broaching of the femoral canal. The robotic arm will be inserted through the incision, especially during acetabulum preparation.
- Your surgeon will use the robotic arm to remove the remaining damaged or arthritic bone and cartilage from the hip joint, using specialised instruments and guidance from the virtual model.
- Based on the virtual model and surgical plan, your surgeon will precisely use the robotic arm to place the artificial implant in the hip joint. The acetabular implant is typically made of Chromium, Cobalt and Titanium 3D Printed coated to guarantee proper press fit fixation and later osseointegration. High Cross-Linked Polyethylene liner and ceramic head materials mimic the hip joint's natural structure and function.
- After the implant is placed, the arthroplasty's stability will be confirmed. Once your surgeon is happy with the achieved parameters, he will close the incision with stitches and apply a water-sealed dressing.
Post-operative Care
- Pain management: After the surgery, you may experience pain, discomfort, and swelling, which can be managed with pain medications, ice therapy, and leg elevation. Your healthcare team will provide you with instructions on how to manage pain effectively.
- Wound care: You will need to keep the surgical incision clean and dry and change the dressing as instructed by your surgeon. You should also monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, or drainage, and immediately report any concerns to your surgeon.
- Physical therapy is crucial to the rehabilitation after robotic total hip replacement surgery. Your physical therapist will work with you to develop a customised exercise program that includes range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and functional activities to improve your hip function and mobility. Usually, they are home-based in the first two weeks, and when your confidence and mobility level increase, you can start visiting your physiotherapist.
- Assistive devices: You may need to use crutches, a walker, or a cane to assist with walking and balance during the early stages of rehabilitation. Your physical therapist will instruct you on using these devices safely and effectively.
- Lifestyle modifications: You may need to make some lifestyle modifications to accommodate the surgery and rehabilitation, such as avoiding high-impact activities, maintaining a healthy weight, and modifying your home environment to prevent falls and accidents. Follow the link for more activity modification instructions. A swimming pool is not recommended before three weeks or when the wound is completely healed.
- Follow-up appointments: You must attend follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress, assess the wound healing and check the implant's stability and function. You should also report any new symptoms or concerns to your surgeon, such as pain, swelling, or difficulty walking.
- Avoid certain activities: It's important to avoid certain activities during the early stages of recovery, such as twisting or bending the hip, lifting heavy objects, or standing for extended periods. Your healthcare team will provide specific guidelines for activity restrictions and limitations.
- Driving is allowed when patients are not taking narcotics/opioids for pain relief. Usually, patients return to driving around 4-6 weeks post-surgery.
Mako Robotic Hip Surgery
Over the years, joint replacement techniques and instrumentation have undergone countless improvements. Mako Technology is designed to help surgeons provide patients with a personalised surgical experience based on their specific diagnosis and anatomy.
How Mako Technology works
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Technology provides a personalised surgical plan based on your unique anatomy. First, a CT scan of the diseased joint is taken. This CT scan is uploaded into the Mako System software, where a 3D model of your hip is created. This 3D model is used to pre-plan and assist your surgeon in performing your total hip replacement.
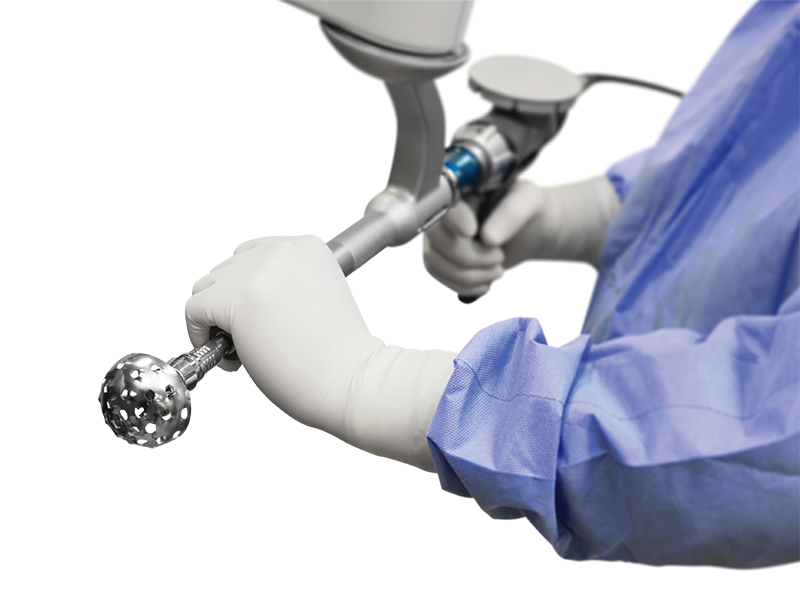
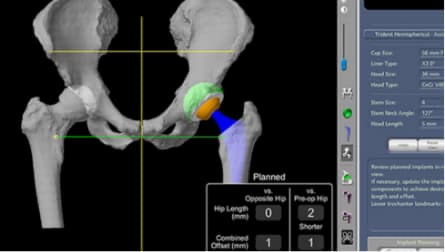
In the operating room, your surgeon follows your personalised surgical plan while preparing the bone for the implant. The surgeon guides the robotic arm within the pre-defined area and the Mako System. The surgeon guides the robotic arm within the predefined area. The Mako System helps the surgeon stay within the planned boundaries defined when the personalised pre-operative plan was created. This helps to provide more accurate placement and alignment of your implant.
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Hip replacement is a surgical procedure for patients suffering from a non-inflammatory or inflammatory degenerative joint disease (DJD). Some forms of DJD include osteoarthritis (OA), post-traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), avascular necrosis (AVN) and hip dysplasia.
The surgery is performed by an orthopaedic surgeon, who guides the surgeon-controlled robotic arm during the surgery to position the implant in the hip joint. The Mako Robotic Arm does not perform surgery, make decisions independently, or move without the surgeon guiding the robotic arm. The Mako System also allows your surgeon to adjust your plan during surgery as needed.
Robotic Total Hip Replacement Prognosis
The prognosis for Robotic Total Hip Replacement is generally good, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life after the surgery. According to the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons, over 90% of patients who undergo hip replacement surgery report satisfaction with the results. The long-term success of the surgery depends on various factors, such as age, health status, lifestyle, and implant design. Still, many patients enjoy long-lasting benefits for over 20 years after the surgery.
Robotic Total Hip Replacement Risks
As with any surgical procedure, robotic total hip replacement carries some risks and potential complications, including:
- Implant dislocation or loosening
- Infection
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
- Leg length discrepancy
- Fracture or bone loss
- Bleeding
- Anaesthesia-related complications
- Blood clots
- Pain and discomfort
- Scar formation
- Rehabilitation challenges
What if Robotic Total Hip Replacement is Delayed?
Delaying Robotic Total Hip Replacement surgery may affect the quality of life, mobility, and overall health. If the hip joint is severely damaged or arthritic, delaying surgery may lead to increased pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, interfering with daily activities and reducing the patient's independence.
Delaying surgery may also increase the risk of complications, such as implant wear, dislocation, or bone loss, which may require more extensive and costly revision surgery. Therefore, consulting with an experienced orthopaedic surgeon and discussing the best timing for Robotic Total Hip Replacement surgery based on the specific condition, age, and lifestyle is essential.








